41 what is the main force that drives deep ocean currents
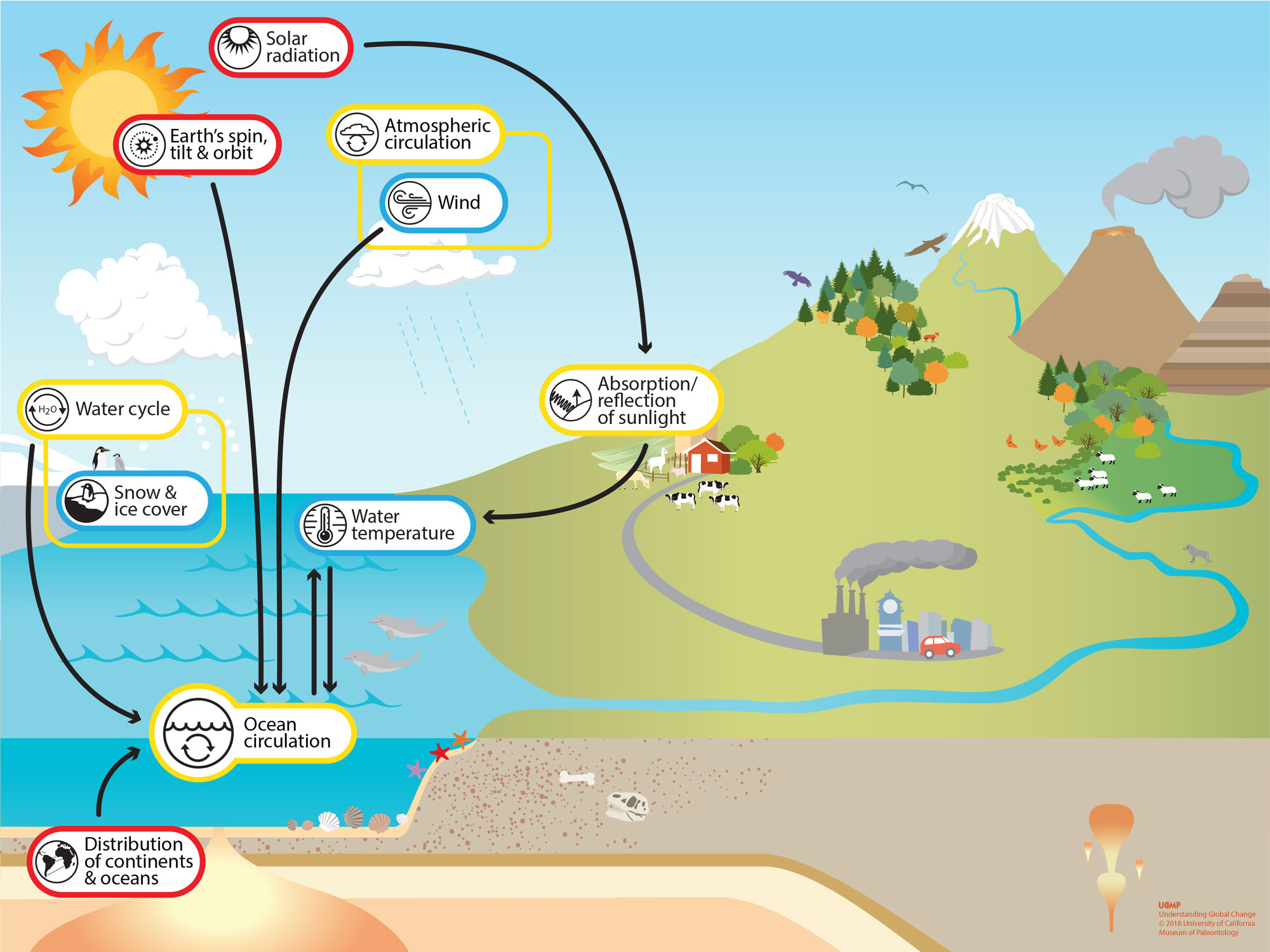
2. Energy in Physical Processes - Teaching Energy 2.3 Earth's weather and climate are mostly driven by energy from the Sun. For example, unequal warming of Earth's surface and atmosphere by the Sun drives convection within the atmosphere, producing winds, and influencing ocean currents. 2.4 Water plays a major role in the storage and transfer of energy in the Earth system. What are Ocean Currents? - Definition & Types - Video ... When you drop about 1,300 feet below the surface, deep water currents move the ocean's water. These currents move much slower, and the forces that drive deep water currents differ from the forces ...
How an "underwater waterfall" came to exist on Mauritius ... And when the ocean currents drive that coastal sand off of the southern tip of Mauritius and into the deep ocean waters, what appears to be an "underwater waterfall" is actually the result of ...

What is the main force that drives deep ocean currents
Ocean motion: Wind-driven currents | National Oceanic and ... Background. Winds, water density, and tides all drive ocean currents. Coastal and sea floor features influence their location, direction, and speed. Earth's rotation results in the Coriolis Effect which also influences ocean currents. Large-scale, surface ocean currents are driven by global wind systems that are fueled by energy from the sun. › topics › engineeringOcean Energy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics A wide range of technologies are possible, including (1) barrages for tidal range utilization, (2) submarine turbines for tidal and ocean currents, (3) heat exchangers for ocean thermal energy conversion, and (4) a variety of devices to harness the energy of waves and salinity gradients (see, e.g., Frigaard et al. 2008). Ocean technologies ... Learning About Renewable Energy | U.S. Department of the ... Deep ocean currents, waves and winds all are a result of the sun's radiant energy and differential heating of the Earth's surface and oceans. The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management is responsible for offshore renewable energy development in federal waters. While there are no commercial solar energy facilities currently operating offshore, BOEM ...
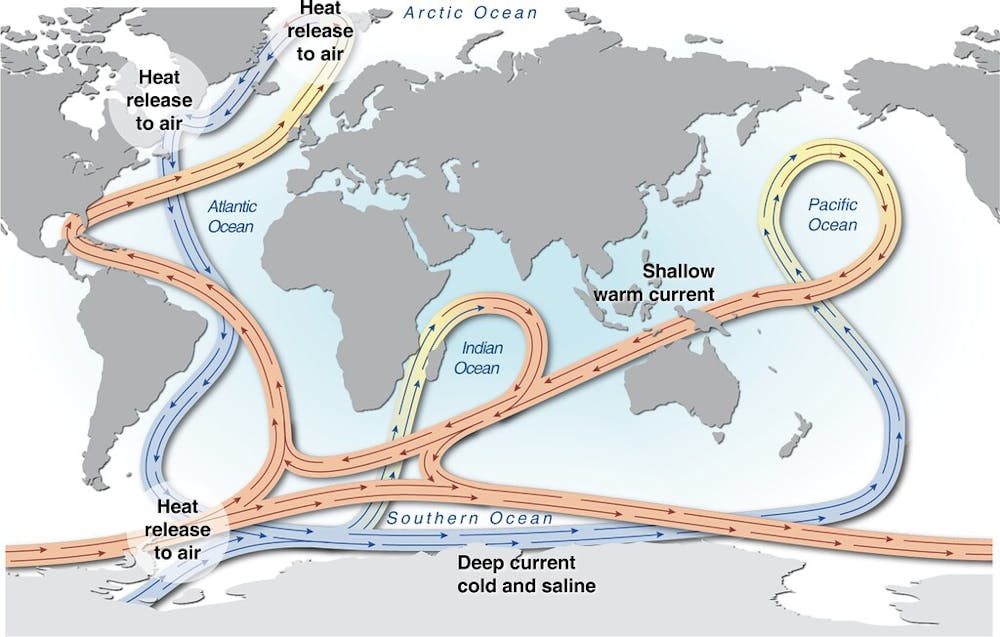
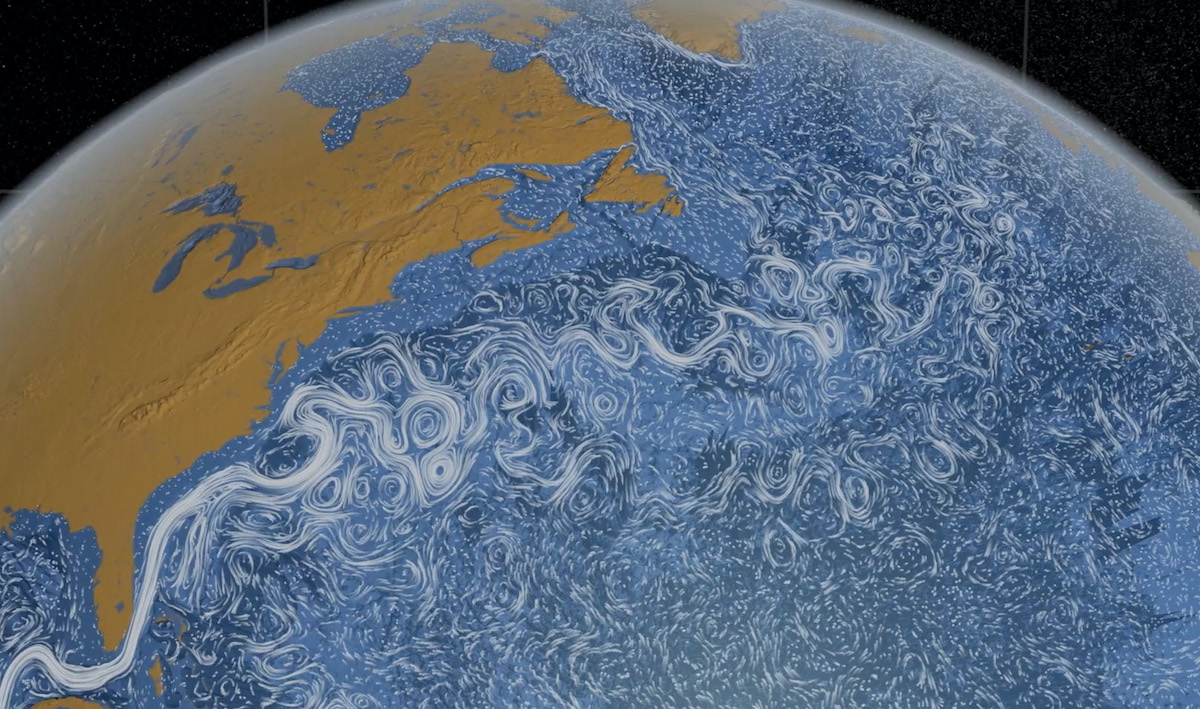
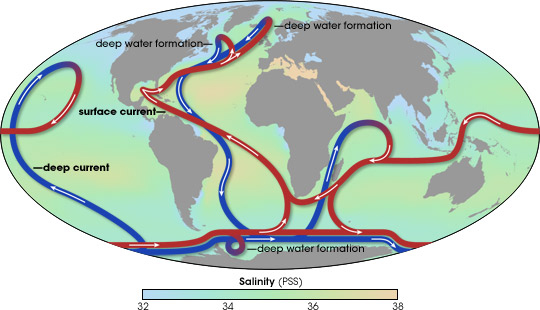
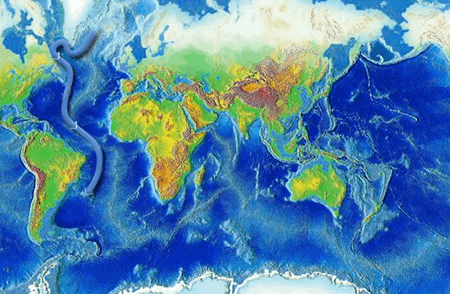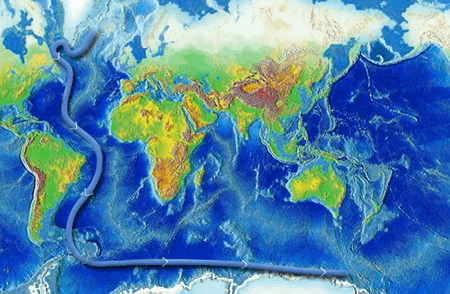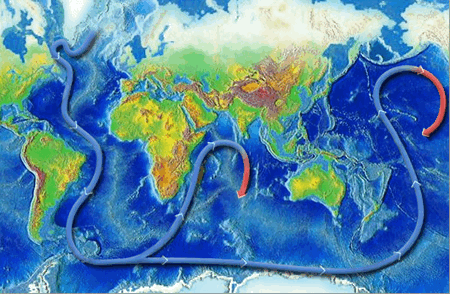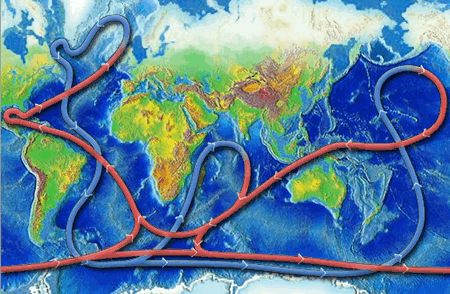
What is the main force that drives deep ocean currents. Plate tectonics - Wikipedia Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin: tectonicus, from the Ancient Greek: τεκτονικός, lit. 'pertaining to building') is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large tectonic plates which have been slowly moving since about 3.4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of continental drift, an idea developed ... With worsening storms, can the Outer Banks protect its ... Timothy Shank is a deep-sea biologist, Associate Scientist in the Biology Department, and former Director of the Ocean Exploration Institute at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. He is known for his research on the ecology and evolution of fauna in deep-ocean hydrothermal, seamount, canyon and deep trench systems. The Sun as a Source of Energy for Winds, Currents & the ... The Sun's Energy for Ocean Currents. The same thing happens with the ocean currents. An ocean current is a continuous flow of water in a particular direction. You can liken it to wind, except this ... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Thermohaline_circulationThermohaline circulation - Wikipedia Driven by the density gradients this sets up the main driving force behind deep ocean currents like the deep western boundary current (DWBC). The thermohaline circulation is mainly driven by the formation of deep water masses in the North Atlantic and the Southern Ocean caused by differences in temperature and salinity of the water.
› physics › convection-currentsConvection Currents - What are Convection Currents ... Convection currents transfer the heat through the mass movement of fluids such as water, molten rock, or air from one place to the other. Convection in Ocean. In the oceans, the convection drives ocean currents like the Gulf Stream and the other currents which turn over and mix up the waters. The hidden melting of the most important ice on Earth ... There are two main kinds of ice that shape sea levels. The first is sea ice, which comes from ocean water that freezes solid. It makes up most of the ice at the North Pole. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › TideTide - Wikipedia Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and the Sun, and the rotation of the Earth.. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or "tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the ... Ocean Circulation: Patterns & Effect on Climate - Video ... Ocean currents travel at both the surface of the ocean, as well as deep within the ocean basin. Currents are influenced by factors such as wind, the rotation of the earth, differences in the water ...
How Can We Use Ocean Energy to Generate Electricity ... The oceans represent almost 70% of the surface of our planet, and they are in constant movement through waves, tides, and currents. These movements are formed differently: waves develop because of the action of the wind; tides because of the moon and the sun, and currents because of differences in water temperature and the rotation of the planet. Ocean movements bring food and oxygen to the ... Mantle Convection: Earth's Plate Tectonic Conveyor Belt ... As mantle convection rises, it breaks apart the Earth to form mid-oceanic ridges (tensional force). When it sinks down, it breaks it apart (compressional force). These tensional and compressional forces are what drives plate tectonics. They break apart the whole lithosphere into 7 major plate tectonics and 12 or so minor ones. Ask NASA Climate - Climate Change: Vital Signs of the Planet Ocean heat content in 2018 compared to the 1955-2006 average. Orange and blue areas show where the upper 700 meters (2,300 feet) of the global ocean gained or lost up to 3 gigajoules (109 joules) of heat energy per square meter compared to the long-term average. Warming of ocean water is raising global sea level because water expands when it warms. › article › 2019Ten things that affect our climate – Science in School Jun 11, 2019 · Ocean currents and wind systems are important components of the climate system. As a result of differential heating, whereby the equator is hotter than the Earth’s poles, convection currents in the oceans and the atmosphere move thermal energy towards the poles. This is the driving force behind atmospheric circulation and the thermohaline ...
Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans: Accepted Articles First Published: 20 April 2022. Key Points. Ocean extremes characterized by exceptionally low pH and aragonite saturation states (OAXs) are identified and tracked in space and time. In the California Current System 3% of OAXs are large coherent structures that last for several years and can propagate over 3000 km.
Want to avoid a bluebottle sting? Here's how to predict ... Currents drive a bluebottle's long tentacles below the ocean's surface and wind drives the sail above it. The bluebottle as a sailboat A bluebottle's body, including the tentacles, is not aligned ...
Ocean - Wikipedia The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. Another definition is "any of the large bodies of water into which the great ocean is divided". Separate names are used to identify five different areas of the ocean: Pacific (the largest), Atlantic, Indian, Southern (Antarctic), and ...
› encyclopedia › ocean-gyreOcean Gyre - National Geographic Society The Earth’s rotation deflects, or changes the direction of, these wind-driven currents. This deflection is a part of the Coriolis effect. The Coriolis effect shifts surface currents by angles of about 45 degrees. In the Northern Hemisphere, ocean currents are deflected to the right, in
Climate Change Indicators: Oceans - US EPA Changes in ocean temperatures and currents brought about by climate change will lead to alterations in climate patterns around the world. For example, warmer waters may promote the development of stronger storms in the tropics, which can cause property damage and loss of life. The impacts associated with sea level rise and stronger storm surges ...
6A: Down to the Deep - The Ocean's Biological Pump Oceans and the Carbon Cycle Part A: Down to the Deep - The Ocean's Biological Pump. Oceans have a large capacity to absorb CO 2, thus reducing the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere and bringing carbon atoms into the ocean system. Many CO 2 molecules that diffuse into sea surface waters diffuse back to the atmosphere on very short time scales. However, some of the carbon atoms from these ...
A strong air mass transport event is now bringing unusual ... PRESSURE DRIVES THE WEATHER ... As we now know, the wind is the main force that is generated by the imbalance in pressure. The image below shows the 5-day wind forecast. ... Below we have an image, which shows the warm ocean currents extending from the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic into the Polar Circle.
Wind - Wikipedia Historically, the Beaufort wind force scale (created by Beaufort) provides an empirical description of wind speed based on observed sea conditions.Originally it was a 13-level scale (0-12), but during the 1940s, the scale was expanded to 18 levels (0-17). There are general terms that differentiate winds of different average speeds such as a breeze, a gale, a storm, or a hurricane.
MoA - The Ukraine Is Still Losing So What Is Its Plan? On April 2, the Russian invaders destroyed the infrastructure of the Kremenchug oil refinery with their shelling, and it stopped working. The damage done daily to the Ukrainian military and military industry is huge. One can get a sense of it when one reads through the briefings of the Russian defense ministry.
Deep Argo: Diving for Answers in the Ocean's Abyss - climate Unlike the last generation of Argo robots—aluminum, cylinder-shaped floats—the new Deep Argo floats, designed by Scripps Institution of Oceanography and Teledyne-Webb Research, can withstand the crushing forces of the deep ocean. Steve Piotrowicz, Program Manager of the U.S. Argo program since 2000, has watched the float design evolve to a ...
News: Ocean Exploration News: NOAA Office of Ocean ... The Labrador Sea plays a vital role in supplying oxygen to deep-sea life across the world. Now, a Canadian-German team has, for the first time, measured the amount of oxygen exiting the Labrador Sea basin, using data from a deep-ocean current. Take a look at the deepest known squid, just found . February 21, 2022 | Freethink
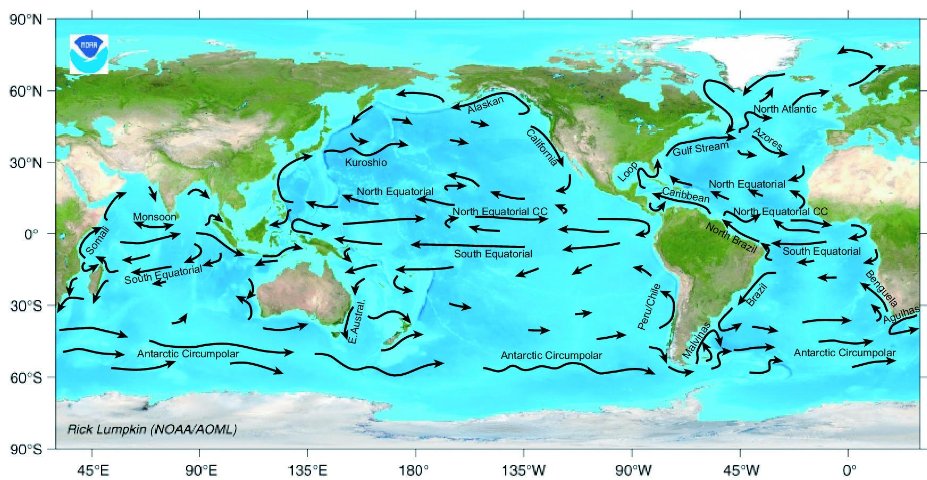
Ocean current - Wikipedia An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water ...
Ocean circulation - MarineSpecies Traits Wiki There are two main types of ocean currents: currents driven mainly by wind and currents mainly driven by density differences. Density depends on temperature and salinity of the water. Cold and salty water is dense and will sink. Warm and less salty water will float. Although tides are generally a dominant driver of water motion in shallow ...
Which Current Moves Cold Water To Warm Latitudes 1.3 THE OCEAN CIRCULATION. Just as winds move through the atmosphere, there are currents in the oceans. These too transport an immense amount of heat from the equator towards the higher latitudes. For the most part, ocean currents only exist because winds blow them along, pushing the water by friction.
› environmentEnvironment - The Telegraph Apr 27, 2022 · Find all the latest news on the environment and climate change from the Telegraph. Including daily emissions and pollution data.
Surface warming-induced global acceleration of upper ocean ... The upper ocean circulation is largely wind driven. Naturally, most studies have so far focused on the effect of wind change, but the projected change in the atmospheric circulation suffers from large uncertainties (fig. S1) (5, 6).Surface buoyancy (heat and freshwater) forcing could become important in regulating ocean circulation under global warming (7-9).
Learning About Renewable Energy | U.S. Department of the ... Deep ocean currents, waves and winds all are a result of the sun's radiant energy and differential heating of the Earth's surface and oceans. The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management is responsible for offshore renewable energy development in federal waters. While there are no commercial solar energy facilities currently operating offshore, BOEM ...
› topics › engineeringOcean Energy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics A wide range of technologies are possible, including (1) barrages for tidal range utilization, (2) submarine turbines for tidal and ocean currents, (3) heat exchangers for ocean thermal energy conversion, and (4) a variety of devices to harness the energy of waves and salinity gradients (see, e.g., Frigaard et al. 2008). Ocean technologies ...
Ocean motion: Wind-driven currents | National Oceanic and ... Background. Winds, water density, and tides all drive ocean currents. Coastal and sea floor features influence their location, direction, and speed. Earth's rotation results in the Coriolis Effect which also influences ocean currents. Large-scale, surface ocean currents are driven by global wind systems that are fueled by energy from the sun.






















0 Response to "41 what is the main force that drives deep ocean currents"
Post a Comment